Navigating The World Of 3D Rendering: A Comprehensive Guide
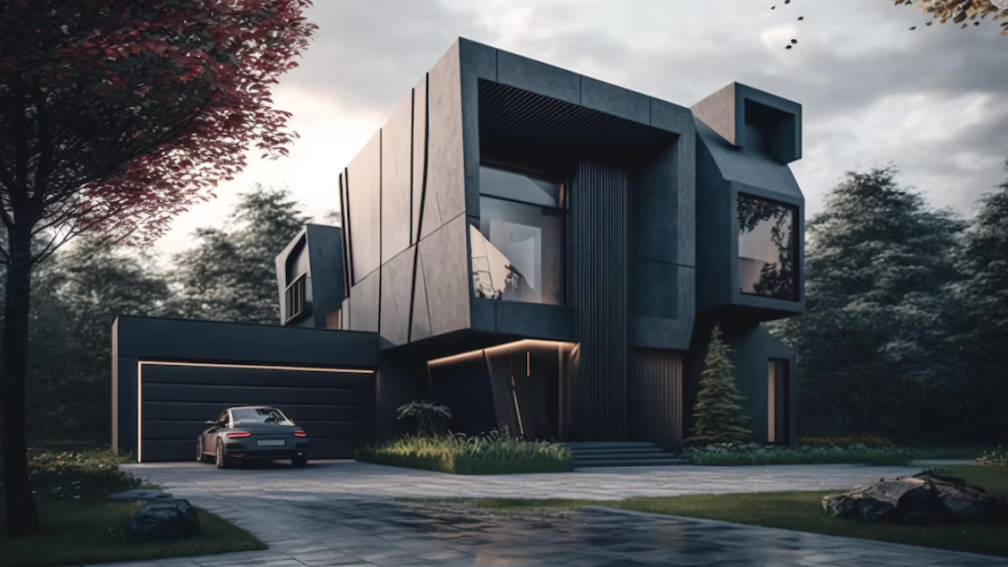

In the realm of design and visualization, 3D rendering stands as a cornerstone, revolutionizing how architects, designers, engineers, and artists bring their ideas to life.
The evolution of technology has propelled this field forward, offering sophisticated tools and techniques that cater to various industries.
From architectural marvels to industrial designs, 3D rendering plays a pivotal role in conceptualization, presentation, and execution.
This comprehensive guide aims to navigate through the intricate landscape of 3D rendering, shedding light on its applications, techniques, and the transformative impact it has on diverse sectors.
Understanding The Essence Of 3D Rendering
At its core, 3D rendering is the process of generating a two-dimensional image or animation from a 3D model. This intricate procedure involves manipulating light, textures, and materials to create realistic visualizations.
Whether it’s architectural structures, product designs, or immersive environments, 3D rendering provides a powerful medium to showcase ideas with unparalleled fidelity and detail.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of 3D rendering transcends boundaries, catering to a multitude of industries with unique requirements. In the realm of architecture, 3D rendering serves as a cornerstone for visualizing building designs and landscapes.
Architectural firms leverage advanced rendering techniques to create lifelike representations of structures, enabling clients to envision projects before groundbreaking commences.
The advent of architectural 3D rendering services has streamlined the design process, offering customizable solutions tailored to the specific needs of clients.
Similarly, in the realm of product design and manufacturing, 3D rendering plays a pivotal role in prototyping and marketing. Industrial designers harness the power of 3D rendering to conceptualize products, iterate designs, and simulate real-world scenarios.
The precision and accuracy offered by 3D industrial rendering streamline the product development lifecycle, reducing time-to-market and enhancing product quality.
Entertainment and media industries also heavily rely on 3D rendering to craft immersive experiences. From blockbuster films to video games, 3D rendering breathes life into fantastical worlds and characters, captivating audiences worldwide.
The meticulous attention to detail and realism achieved through rendering technologies elevate storytelling and visual aesthetics, setting new benchmarks for cinematic excellence.
Techniques And Tools Of The Trade
Mastering the art of 3D rendering requires proficiency in a myriad of techniques and tools. From modeling and texturing to lighting and rendering, each stage of the process demands meticulous attention to detail.
Leading software platforms such as Plus Render, Autodesk Maya, Blender, and Cinema 4D offer a robust suite of tools tailored to the needs of 3D artists and designers.
Modeling serves as the foundation of 3D rendering, allowing artists to create digital representations of objects and environments. Whether it’s sculpting organic shapes or designing intricate architectural structures, modeling techniques vary based on the complexity of the project.
Advanced modeling tools enable artists to manipulate vertices, edges, and polygons with precision, bringing their vision to fruition.
Texturing adds depth and realism to 3D models by applying surface properties such as color, texture, and reflectivity. From rough concrete to polished metal, textures imbue objects with tactile qualities, enhancing visual fidelity.
Texture mapping techniques such as UV mapping and procedural texturing offer unprecedented control over surface detailing, allowing artists to achieve photorealistic results.
Lighting plays a crucial role in 3D rendering, influencing mood, atmosphere, and visual impact. Whether it’s natural sunlight streaming through windows or artificial lamps illuminating interiors, lighting setups can make or break a rendering.
Advanced rendering engines offer a plethora of lighting options, including global illumination, ambient occlusion, and volumetric lighting, enabling artists to create compelling visual narratives.
Rendering is the final stage of the 3D rendering pipeline, where the magic truly happens. Rendering engines such as Plus Render, V-Ray, Arnold, and Octane utilize sophisticated algorithms to simulate the behavior of light and materials, producing stunningly realistic images.
With features such as ray tracing, depth of field, and motion blur, modern rendering engines push the boundaries of visual fidelity, blurring the line between reality and simulation.
The Future

As technology continues to evolve, the future of 3D rendering holds limitless possibilities. Advancements in real-time rendering engines are revolutionizing industries such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive media.
With the rise of cloud computing and distributed rendering, rendering workflows are becoming more efficient and scalable, empowering artists to tackle projects of unprecedented scale and complexity.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning promises to redefine the landscape of 3D rendering. From automated asset generation to intelligent scene composition, AI-driven tools are streamlining workflows and enhancing creativity.
With the advent of generative adversarial networks (GANs) and neural rendering techniques, the boundaries of what’s possible in 3D rendering are being continuously pushed, opening new avenues for innovation and expression.
The Evolution of 3D Rendering Technology
Over the decades, 3D rendering technology has undergone a remarkable evolution, driven by advancements in computing power, software development, and rendering algorithms. In the early days of computer graphics, rendering was a time-consuming process, limited by the computational capabilities of the era.
However, with the advent of dedicated graphics hardware and parallel processing architectures, rendering speeds accelerated dramatically, paving the way for real-time visualization and interactive experiences.
One significant milestone in the evolution of 3D rendering technology is the introduction of ray tracing algorithms. Traditionally used in offline rendering, ray tracing simulates the physical behavior of light, producing highly realistic images with accurate reflections, refractions, and shadows.
While computationally intensive, recent breakthroughs in hardware acceleration and algorithm optimization have made real-time ray tracing a reality, revolutionizing industries such as gaming, automotive design, and architectural visualization.
Another pivotal development in 3D rendering technology is the emergence of physically based rendering (PBR) techniques. Unlike traditional rendering methods that rely on ad-hoc approximations, PBR simulates the interaction between light and materials based on real-world physics principles.
This approach yields photorealistic results with accurate surface properties such as reflectivity, roughness, and subsurface scattering. With the widespread adoption of PBR workflows in software packages like Substance Painter and Unreal Engine, artists can achieve unprecedented levels of realism and fidelity in their renderings.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of 3D rendering requires a blend of technical expertise, creative vision, and relentless curiosity. From architectural marvels to industrial designs, 3D rendering serves as a cornerstone for visual storytelling and innovation across diverse industries.
By harnessing the power of advanced techniques and tools, artists and designers can bring their ideas to life with unparalleled fidelity and impact. As we venture into the future, the transformative potential of 3D rendering continues to inspire and captivate, shaping the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
Read Also:

























Leave A Reply